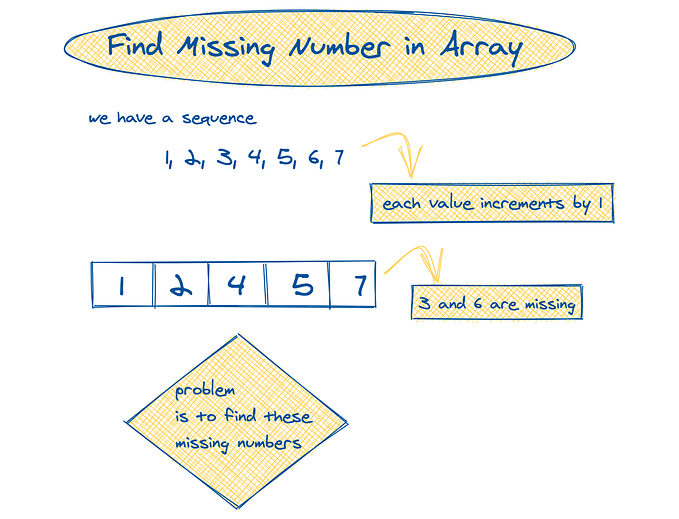
Find the Unsorted Array Portion
It is another week so it is time to show how to solve another algorithm. From Leet Code, given an array nums, find the length of the continuous unsorted subarray. For example, given the array
var nums = [2,6,4,8,10,9,15]the output will be
output: 5in which the unsorted numbers in the array are
[6, 4, 8, 10, 9]. First off, we call a new array that is equal to the nums and sort it
const arr = [...nums]
var array = arr.sort((a, b) => a - b)The next step is to assign a couple values
let firstIndex = null
let lastIndex = nums.length - 1.We will explain why firstIndex is null instead of 0 later. What we want to do is find the first and lastpoint in the array where the element is in the wrong spot when compared to the sorted array. The code for this is
for (let i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (nums[i] !== array[i]) {
firstIndex = i
break
}
}for (let i = lastIndex; i >= 0; i--) {
if (nums[i] !== array[i]) {
lastIndex = i
break
}
}
return lastIndex + 1 - firstIndex.
We have to add 1 because we go from 0 to the length minus 1. If that were not the case, we do not need to add 1.
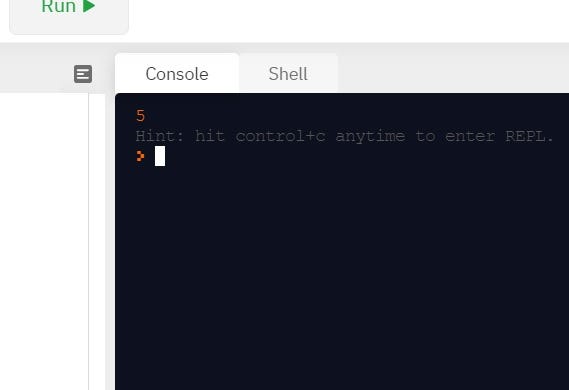
Let’s test it out with the array above. The output should be 5 and figure 1 is indeed 5.
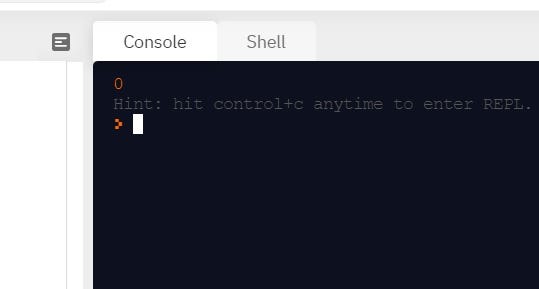
However, we are not done yet. Wat about an array like
[1,2,3,4]?The answer should be 0, and figure 2 shows 0.
Now back to the question of why firstIndex is set to null instead of 0. The problem with firstIndex set to 0 is that the array
[1,2,3,4]will appear unsorted. With null, firstIndex will stay null because everything is in order.
Finally, let an array be of length 1. This is simple, and the code is
if (nums.length === 1) {
return 0
}.Full code is
function findUnsortedSubarray(nums) {
if (nums.length === 1) {
return 0
} const arr = [...nums]
var array = arr.sort((a, b) => a - b)
let firstIndex = null
let lastIndex = nums.length - 1 for (let i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (nums[i] !== array[i]) {
firstIndex = i
break
}
}
if (firstIndex === null ) {
return 0
}
for (let i = lastIndex; i >= 0; i--) {
if (nums[i] !== array[i]) {
lastIndex = i
break
}
}
return lastIndex + 1 - firstIndex
};
This solution has passed all tests on Leet Code.
References